URL Namespace
URL 네임스페이스 적용
Django에서는 동일한 URL 네임을 사용하는 경우 네임스페이스를 지정하여 앱별로 URL을 고유하게 관리할 수 있도록 지원
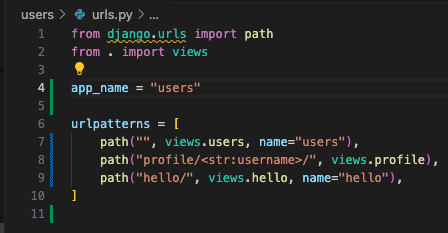
1. 각 'urls.py'에 'app_name'을 정의
2. 템플릿 및 코드에서 'namespace:url_name' 형식으로 URL을 참조
- 'articles'와 'users'앱에 각각 'hello/'라는 동일한 URL 패턴이 있는경우


'articles/hello/'와 'users/hello'가 서로 다른 경로이므로 기본적으로 구별이 됨
하지만 템플릿에서 URL을 참조할 때 문제가 발생

Index라는 template에서
{% url 'hello' %}
혹은
views에서
redirect('hello')
이렇게 작업할 시
Django는 URL 패턴을 찾을 때
프로젝트의 urls.py에서 urlpatterns에 등록된 순서대로 URL을 탐색
→등록된 순서에 따라 먼저 일치하는 패턴이 실행됨
# 프로젝트 루트 urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path("admin/", admin.site.urls),
path("articles/", include("articles.urls")), # ✅ 먼저 탐색됨
path("users/", include("users.urls")), # ✅ 다음 탐색됨
path("", include("homepage.urls")), # ✅ 마지막으로 탐색됨 (루트 URL)
]
Django의 Templates탐색 순서는 TEMPLATES 설정의 APP_DIRS 값에 따라 다르지만
TEMPLATES = [
{
"BACKEND": "django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates",
"DIRS": [],
"APP_DIRS": True, # ✅ 앱 내부의 templates 폴더를 자동으로 탐색
},
]이렇게 APP_DIRS=TRUE (기본 설정)인 경우
프로젝트폴더의 루트디렉토리 settings.py - INSTALLED_APPS의 등록 순서대로 templates/폴더를 탐색함
→articles앱의 hello.html가 렌더링 됨



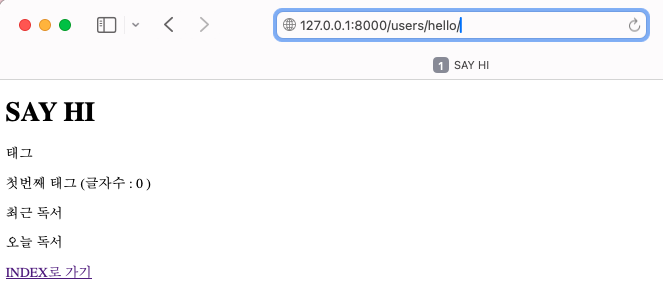
원하는 URL을 명확하게 지정하려면 URL 네임스페이스를 사용

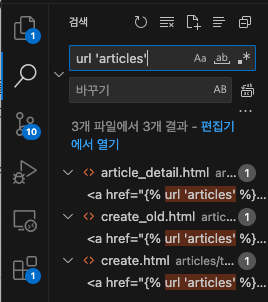
1. urlpatterns 안에 적혀있는 articles부터 data-catch까지 검색해서 하이퍼링크 달려있는것들 전부 검색기능을 사용해 찾아주고
2.
{% url 'articles' %}이렇게 돼있던걸
{% url 'articles:articles' %}이런식으로 바꿔줌
3.
redirect되는 부분들 (views.py)
redirect('create')이런식의 코드들을
redirect('articles:create')이렇게 바꿔줌
4.
users앱도 마찬가지
처음부터 'app_name'을 지정하고 개발하면 url충돌문제 방지 가능
Template namespace 적용
각 앱의 'templates/' 디렉토리를 앱별 네임스페이스로 구분하는 것이 좋음


이후 템플릿을 참조할 때 앱 네임스페이스를 포함하여 정확한 경로를 지정
veiws.py에서 render부분
return render(request, "update.html")
↓
return render(request, "articles/update.html")
{% extends "articles/index.html" %}{% extends "users/index.html" %}
이렇게 Django가 템플릿을 찾을 때 앱의 네임스페이스를 고려하여 올바른 파일을 불러오도록 참조 방식을 변경
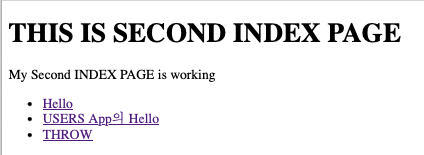
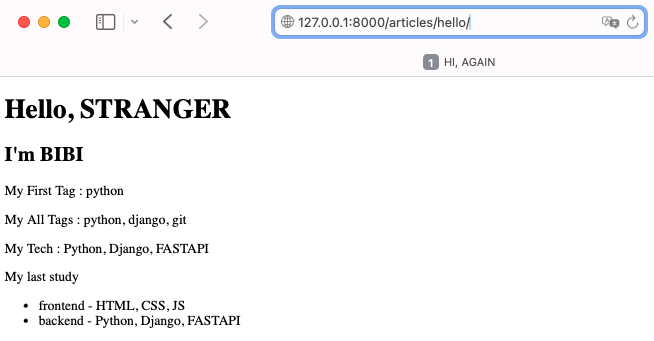
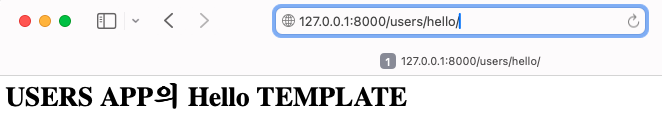
올바른 의도한 URL-의도한 templates
* Templates 구조와 app_name 지정 순서
템플릿(namespace)과 app_name을 설정하는 순서는 프로젝트의 유지보수성을 높이는 데 중요한 역할을 함
Django는 템플릿을 먼저 찾고, URL 네임스페이스를 나중에 확인
→ 템플릿을 먼저 정리하고 app_name을 설정하는 것이 더 깔끔한 접근 방식
✔ 템플릿 충돌 방지: index.html이 여러 개 있어도 구분 가능 → articles/index.html, users/index.html
✔ 앱 간 구조가 명확해짐: 프로젝트가 커질수록 파일 정리 편리
✔ 확장성 증가: 다른 앱에서도 동일한 패턴을 유지할 수 있음
1. 템플릿 네임스페이스 적용 (템플릿 구조 정리)
my_project/
│── articles/
│ ├── templates/
│ │ ├── articles/ # 앱 네임스페이스를 템플릿 안에서 먼저 정리
│ │ │ ├── index.html
│ │ │ ├── list.html
│── users/
│ ├── templates/
│ │ ├── users/
│ │ │ ├── profile.html
│ │ │ ├── index.html✔ Django가 articles/index.html, users/index.html을 정확히 구별
✔ render()
return render(request, "articles/index.html")
return render(request, "users/index.html")
2. app_name을 지정하여 URL 네임스페이스 설정
# articles/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from . import views
app_name = "articles"
urlpatterns = [
path("", views.index, name="index"),
path("hello/", views.hello, name="hello"),
]✔ app_name을 설정하면 {% url 'articles:index' %}처럼 사용 가능
**app_name을 먼저 정하면 발생할 수 있는 문제점
템플릿 경로가 중복되거나 충돌이 발생할 가능성이 높아짐
템플릿 구조를 먼저 정리하지 않고, app_name을 먼저 설정한 경우
app_name = "articles"
urlpatterns = [
path("", views.index, name="index"),
]return render(request, "index.html") # 충돌 가능성 있음✔ Django가 index.html을 찾을 때 어떤 앱의 템플릿인지 모르게 됨
✔ 이후에 템플릿 네임스페이스를 다시 정리해야 하는 번거로움이 생김
템플릿 네임스페이스(templates/app_name/) 정리
각 앱의 app_name 지정 -URL 네임 스페이스 설정
Django의 render()에서 네임스페이스를 포함한 경로 사용(app_name/template.html)
템플릿에서 {% url 'app_name:template' %} 네임스페이스 활용
'∟ Framework > ⊢ Django' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Django - 회원기능 구현하기 (1) | 2025.02.06 |
|---|---|
| Django - Auth (1) | 2025.02.04 |
| Django - Django Form과 ModelForm을 활용한 입력 폼 처리 (0) | 2025.01.31 |
| Django - MTV 패턴을 활용한 RUD(Read, Update, Delete) 구현 (0) | 2025.01.22 |
| Django - MTV패턴을 활용한 C(Create)와 R(Read) 구현 (0) | 2025.01.18 |